RVOT / LVOT tachycardia: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
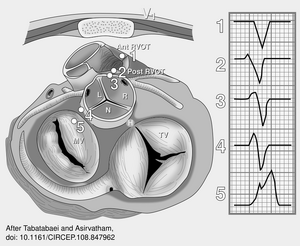
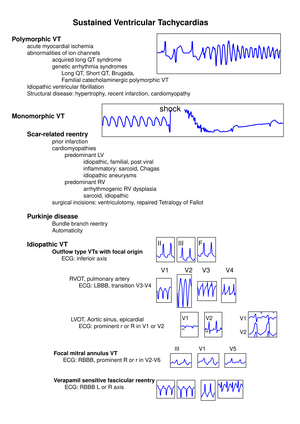
[[File:Stevenson.svg|thumb|ECG types of VT and most common causes are shown with characteristic | [[File:Stevenson.svg|thumb|ECG types of VT and most common causes are shown with characteristic | ||
ECG features of selected VTs. LBBB indicates left bundle-branch block; LVOT, LV outflow tract; RBBB, right bundle-branch block; L, left; and R, right.]] | ECG features of selected VTs. LBBB indicates left bundle-branch block; LVOT, LV outflow tract; RBBB, right bundle-branch block; L, left; and R, right.]] | ||
< | <cite>test</cite> | ||
< | <biblio> | ||
#test pmid=21674797 | |||
</biblio> | |||